|
Cube GUI User Guide
(CubeGUI 4.8.2, revision 7895e762)
Introduction in Cube GUI and its usage
|
|
Cube GUI User Guide
(CubeGUI 4.8.2, revision 7895e762)
Introduction in Cube GUI and its usage
|
Advanced Color Map Plugin provides additional color maps. The configuration dialogs are presented in Figure coloring_acm. For every color map, the plot allows for change of data accepted by color map and one can do that using left and right marker, by dragging the marker or providing exact position through a double click near the marker value (new dialog will appear). The default color for values out of range is grey.
One can change colors of scheme (for some color maps) and color for values out of range. Double mouse click on proper part of the plot opens a dialog with selection of RGB color. Additionally, one can adjust the plot marker or reset to default values through the context menu.
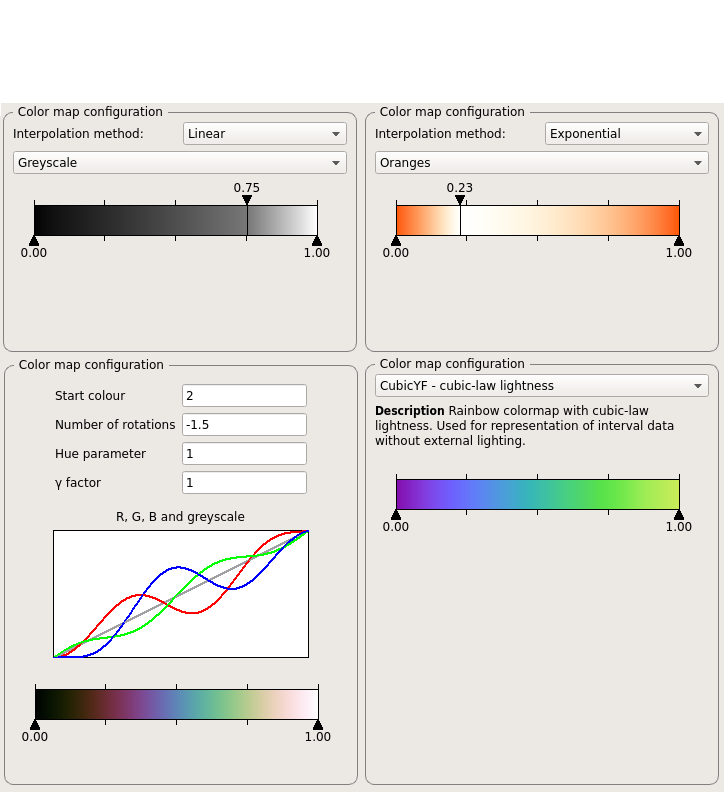
Currently the plugin adds four different sets of color maps:
Sequential: Scheme is defined by starting and ending color with linear or exponential interpolation between them. Predefined schemes provide simple interpolation from one color to pure white. Middle marker allows for subtle change of interpolation.
 |
Copyright © 1998–2022 Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH,
Jülich Supercomputing Centre
Copyright © 2009–2015 German Research School for Simulation Sciences GmbH, Laboratory for Parallel Programming |