Tape Casting
One of the most well-known and used method to manufacture multilayered ceramic components is the doctor-blade tape casting technique. Glenn N. Howatt is regarded as the godfather of tape casting and established this processing method in 1947[1] and also filed the first patent in 1948[2]. A plentiful variety of electronic components like multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC), actuators (MLA), varistors (MLV) or tapes for low/high temperature cofired ceramics (LTCC, HTCC) can be manufactured.
Contents
Components of a tape caster
Tape casting machine
Tape casting machines are assembled in different scales. Usually big industrial companies have continuous tape casters with a length of several hundred meters. However, in academic research much smaller lab-scale tape caster are used which can range from half a meter to several meters in length.
Continuous as well as discontinuous tapes can be prepared with lab-scale tape casters. For continuous tapes, guide rollers and rollers with the carrier substrate are needed. If discontinuous tapes are produced, carrier substrate sheets can be used likewise.
Carrier substrate
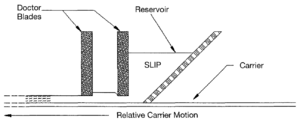
Reservoir
Doctor-blade
Drying chamber
Process of tape casting
Slip delivery
Casting
Drying
Quality assessment
optical check, bubbles, orange peel, cracking, homogeneity, bendable, strechable, handable, homogeneous green sheet thickness, green density
References
- ↑ [1] Howatt, G.N., Breckenridge, R.G. and Brownlow, J.M. (1947), FABRICATION OF THIN CERAMIC SHEETS FOR CAPACITORS. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 30: 237-242.
- ↑ [2] Howatt, G.N., Method of Producing High Dielectric High Insulation Ceramic Plates, U.S. Patent 2,582,993 (filed October 29, 1948).
- ↑ [3] Mistler, R.E. (1995), The principles of tape casting and tape casting applications. In: Terpstra, R.A., Pex, P.P.A.C., de Vries, A.H. (eds) Ceramic Processing. Springer, Dordrecht.
