 |
SIONlib
1.7.7
Scalable I/O library for parallel access to task-local files
|
 |
SIONlib
1.7.7
Scalable I/O library for parallel access to task-local files
|
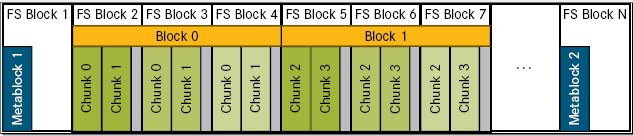
One of the strategies for SIONlib to increase I/O performance is preventing file system block contention, that is different tasks trying to modify the same file system block at the same time. In order to avoid this SIONlib needs additional information from the user when opening a file. The chunksize supplied during the open call is communicated globally and lets SIONlib calculate the ranges inside the file which belongs to each task. In case there is not enough space left for a write request in the current block SIONlib skips all the file ranges that belong to other tasks and has new chunksize bytes of space available. The sparsity of the file that might result from this strategy is handled by the underlying file system which does not allocate blocks for empty parts of the file.
All starting positions of the blocks are aligned to the file system blocksize (e.g. 4 MiB on JSC's GPFS in 2016). The first meta data block META1 contains all static meta data which is independent from the number of chunks. The second meta data block is located at the end of the sion file and contains the data which depends on the number of chunks written by each task. The first meta block will mainly be written while opening the sion file, the second meta data block will be written while closing the file. Each BLOCK contains one chunk of space for each task according to the chunksize specified in sion_open(). There could be gaps between chunks if the requested chunksize is not divisible by the fs blocksize. The size of such a BLOCK including the space for additional alignment space is internally stored in the variable globalskip (see also sion_get_locations).
If a task has reached the end of a chunk while writing data, sion_ensure_free_space will move the filepointer for this task to the next BLOCK. The new position is globalskip bytes from the starting position of the current block and can be computed locally without communication to other tasks. The information how many chunks are used and how many bytes are written in each chunk will be stored in memory until sion_close() is called. This function collects this information from all tasks to task 0 and task 0 writes the data to META2.
| bytes | content | type | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 'sion' | char* | identification of sion file format |
| 4 | 0001 | int | for identification of little/big endianess |
| 4 | version | int | version number of used sion library |
| 4 | version_patchlevel | int | patch level of used sion library |
| 4 | fileformat_version | int | version of sion file format |
| 4 | blocksize | int | fs blocksize used for access to this file |
| 4 | ntasks | int | number of tasks wrote to this file |
| 4 | nfiles | int | number of physical files |
| 4 | filenumber | int | number of current physical files |
| 8 | flag1 | int | not used currently |
| 8 | flag2 | int | not used currently |
| 1024 | filenameprefix | char* | prefix of filename (for multi-file support) |
| 8 | globalrank(1) | long | global unique id for this task 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | globalrank(numpe) | long | global unique id for this task numpe |
| 8 | size(1) | long | chunksize requested by processor 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | size(numpe) | long | chunksize requested by processor numpe |
| 4 | maxchunks | int | maximum number of chunks used |
| 8 | start_of_varheader | long | start position of META2 |
| bytes | content | type | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | chunks(1) | long | number of chunks written from task 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | chunks(numpe) | long | number of chunks written from task numpe |
| 8 | chunksize(1) | long | number of bytes written in chunk 1 from task 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | chunksize(numpe) | long | number of bytes written in chunk 1 from task numpe |
| 8 | chunksize(1) | long | number of bytes written in chunk 2 from task 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | chunksize(numpe) | long | number of bytes written in chunk 2 from task numpe |
| ... | |||
| 8 | chunksize(1) | long | number of bytes written in chunk n from task 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | chunksize(numpe) | long | number of bytes written in chunk n from task numpe |
| If a chunk was not used by a specific task the chunksize value is set to -1. |
| bytes | content | type | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | mapping_size | int | number of global ranks |
| 8 | fnr(1),lrank(1) | 2*int | file number and local for global rank 1 |
| ... | |||
| 8 | fnr(numpe),lrank(numpe) | 2*int | file number and local for global rank numpe |